电化学添加剂制造公司Fabric8Labshas announced the close of a $50M Series B investment.
This round was led byNew Enterprise Associates(NEA),来自现有投资者的参与,包括Intel Capital,imec.XPAND,SE冒险,TDK Ventures, 和Lam Capital。新资金将用于扩大公司专有的电化学添加剂制造(ECAM)技术,并建立了试点生产设施。
Fabric8labs首席执行官兼联合创始人Jeff Herman表示:“我们很高兴能够获得NEA的支持。”“至关重要的是,与我们的使命保持一致的合作伙伴是从根本上转移制造的,以可持续的,添加剂的制造方法转移制造业;我们很幸运地与一群顶级投资者团队在一起。”
How does Fabric8Labs plan on using this investment for ECAM?
NEA的Venture合作伙伴Greg Papadopoulos博士说:“ ECAM在添加剂制造的方法中的真正区分是真正的区别。”“您可以避免昂贵的后处理,在微米级上轻松建造复杂的东西,直接在现有的基板上打印,并以最低的能量(以及碳 - 因此 - 碳)的足迹进行大规模完成所有这些内容。我们很高兴与Jeff和Fabric8labs团队合作,参加这项革命的增材制造业。”
Fabric8labs声称,在过去的十年中,金属添加剂制造业经历了快速发展,平均复合年增长率(CAGR)为27%。但是,由于基于粉末的热过程和原料的局限性,这些过程促进了高成本,重复性不足以及突出分辨率的限制,因此用于大量制造的金属AM的实施受到限制。另一方面,ECAM是由由溶解金属离子组成的水基原料以原子量制造的。通过电化学方法,可以使用复杂的,内部特征,微观尺度分辨率,高纯度材料和快速的可扩展性来协助质量制造。
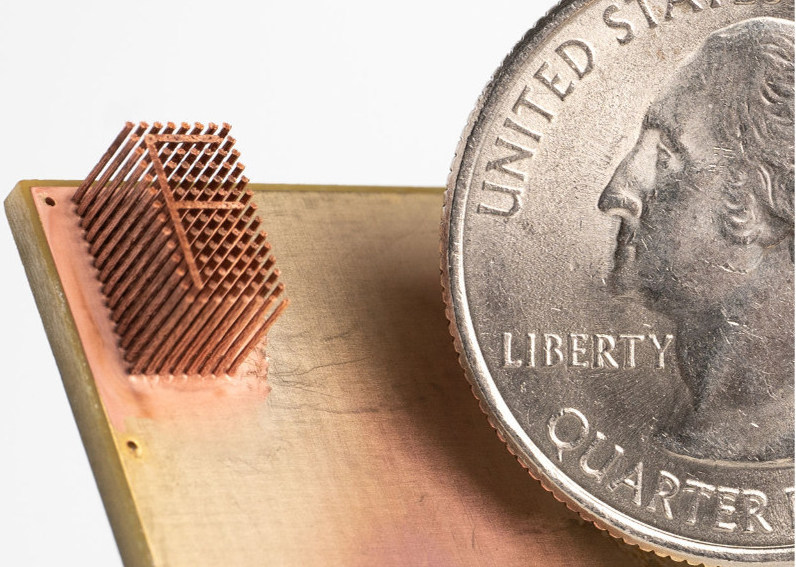
ECAM特别有资格生产超高分辨率,可以明确印刷到温度敏感的基板(如PCB,硅或现有金属零件)上的纯铜零件。该功能发生在电子公司正在寻找能够解决功率密度,热管理,可持续性挑战和设备外形的技术时。ECAM可以创建优化的设计,这些设计与高性能计算(HPC),数据中心,电动汽车,可穿戴设备,RF通信以及各种消费电子产品等最终应用中的越来越严格的性能标准。
ECAM is ecologically responsible and sustains green initiatives in addition to offering manufacturing capabilities that enhance customers’ technology roadmaps. ECAM decreases greenhouse gas emissions by more than 90% when compared to other additive technologies and conventional manufacturing. Customers’ implementation of ECAM across a broad range of market opportunities has been expedited by the “winning combination” of functionality, cost performance, and sustainability.
Intel Capital董事总经理Jennifer Ard说:“ Fabric8labs的新技术的潜力是不可否认的,我们认为ECAM适合于整个电子价值链中的广泛应用。”“随着团队努力扩展其产品,他们将能够为客户跨多个业务部门提供价值,从而进一步提高其增值。”
此外,Fabric8labs还在处理微机械零件和医疗设备应用。这些应用利用ECAM固有的好处的力量来创建极高的,高级的结构和高性能合金。随着公司的发展,ECAM将允许超高分辨率应用程序,例如传感器,增强的手术工具,MEM和诊断设备。

电化学3D打印
Previously,劳伦斯·利弗莫尔国家实验室(LLNL)研究人员开始采用3D打印来创建流通电极(FTES)电化学反应堆,达到反应器改良的性能高达100倍。LLNL团队能够使用直接墨水写作的石墨烯气凝胶制成的3D打印定制的多孔电极。印刷结构对于广泛的电化学反应至关重要,包括将二氧化碳和其他分子转化为有效的能量产物。
Elsewhere, anelectrochemical-based metal 3D printing technique是由一群来自德克萨斯大学达拉斯机械工程系。This method, known as localized pulsed electrodeposition (L-PED), allowed the team to control the metal microstructure in real-time throughout the printing process. L-PED, which is also free of post-processing, improves the electrical and mechanical characteristics of 3D printed pure crystalline metals by adjusting process parameters.
什么是3D打印的未来for the next ten years hold?
What工程挑战will need to be tackled in the additive manufacturing sector in the coming decade?
To stay up to date with the latest 3D printing news, don’t forget to subscribe to the3D打印行业newsletter或跟随我们Twitter, or like our page onFacebook。
While you’re here, why not subscribe to ourYouTube渠道?包括讨论,汇报,视频短裤和网络研讨会重播。
Are you looking for a job in the additive manufacturing industry? Visit3D Printing Jobsfor a selection of roles in the industry.
Feature image shows Fabric8Labs’ technology reportedly yields structures with “superior feature resolution.” Photo via Fabric8Labs.


