的研究人员Osaka Universityand Japanese printing technologies providerToppan使用基于3D打印的新型组织建模技术成功生产了培养的和牛牛肉。
The technology enabled the researchers to replicate the complex tissue structures of Wagyu beef, including muscle, fat and blood vessel tissue, in order to achieve the meat’s unique marbling structure. The aim of the research was to create complex meat structures that truly replicate the structure, texture, and characteristics of individual meats, in order to address the various limitations of current cultured meat production techniques.
The researchers believe their work could also help to address the global increase in food demand, as well as mitigate the impact of contributing factors such as climate change, deforestation and ozone depletion.
“The technology from this research was developed to replicate the complex and beautiful marble structure seen in Japan’s world-renowned Wagyu beef,” said Professor Michiya Matsusaki of Osaka University. “We hope that cultured Wagyu steak meat becomes a new industry for Japan.”
解决“蛋白质危机”
到2050年,全球人口预计将超过97亿,随后,食品需求的增加以及气候变化的影响,这意味着不可能提供足够的食物供应。因此,研究人员认为,世界可能面临所谓的“蛋白质危机”,促使人们对植物性蛋白质和培养的肉类作为替代蛋白质来源的更大兴趣。
Research into cultured meat has been underway for some time, and 3D printing is playing an increasing role in aiding not only the research in this area, but also the commercial production of cultured meat products.
For instance, 3D printed food start-upRedefine Meatrecently launched its first series of3D printed ‘New-Meat’ products到selected restaurants and hotels in Israel, with the rollout planned to extend to Europe later this year, and to the US and Asia in 2022. Meanwhile, fellow food printing start-upSavorEat与全球酒店公司合作Sodexo到pilot its Robot Chef 3D printing technology明年在美国大学的第一款Alt-Meat产品。
在其他地方,食品技术公司MeaTech已经宣布plans to enter chicken fat productionduring 2022 using the technologies gained from itsacquisition of Peace of Meat, a developer of cultured fat products, last year.
3D printing Wagyu beef
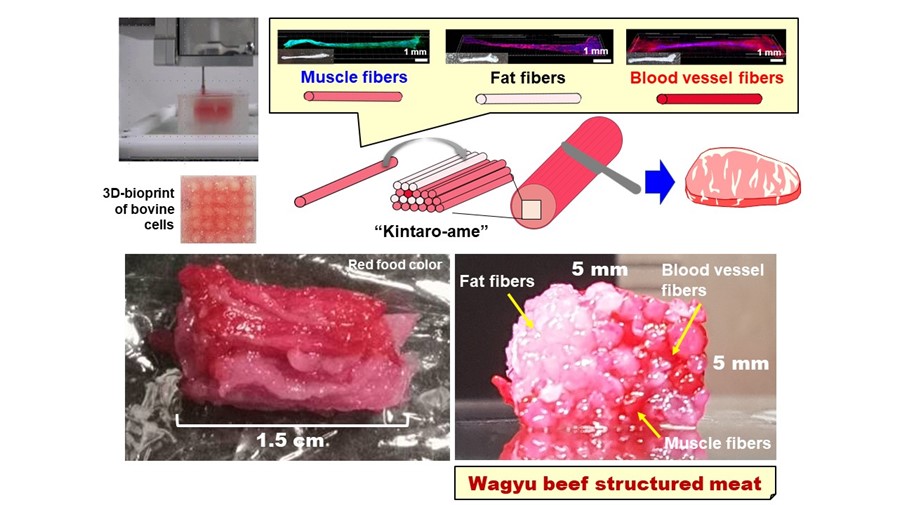
大阪大学和Toppan研究人员试图改善3D印刷肉的结构,他们说,到目前为止,它一直在努力充分复制真正的肉质和层次。他们声称,目前对3D印刷肉类的研究仅产生了仅由肌肉纤维组成的结构,这使其具有碎肉结构,无法准确重新创建单个肉类的特定特征。
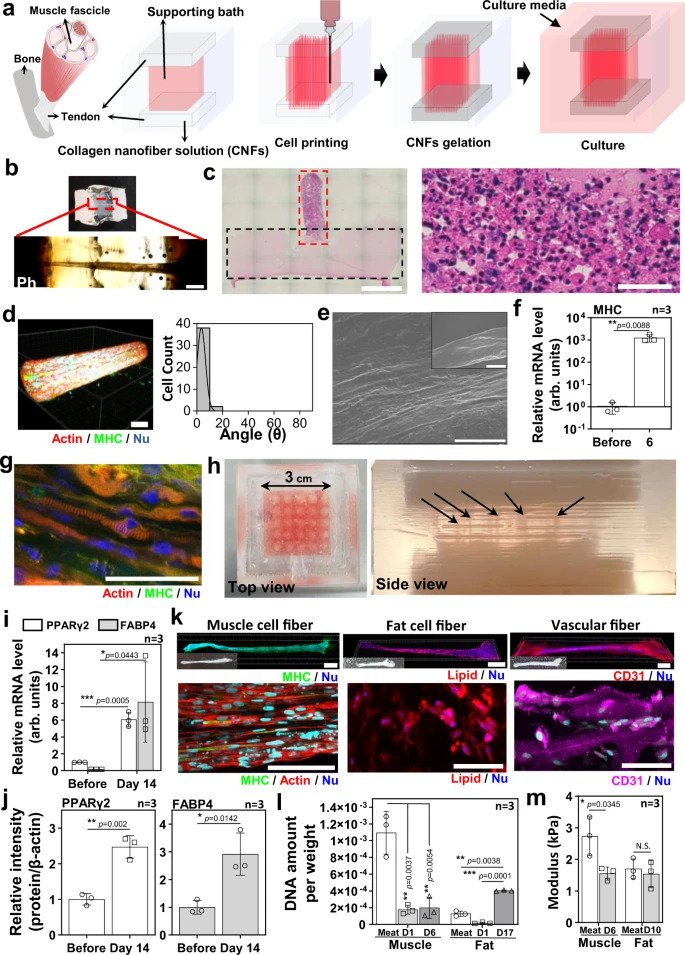
为了解决这个问题,该团队开发了一种原始的组织建模技术,该技术使用3D生物打印来开发类似肌腱的凝胶,可以组装,以制造长10毫米且宽5毫米的牛排状肉结构。研究人员的技术称为肌腱 - 凝胶综合生物打印(TIP),使其能够用不同的组织构成制造肉结构,以更准确地复制其真实的肉类等效物。
“To enable us to use 3D printing technology to stably produce muscle, fat, and blood vessel tissue, it was important to suppress the contraction that occurs during differentiation induction,” said Matsusaki. “Focusing on the fact that tendons support muscles in the body, we therefore produced ‘artificial tendon tissue’ using type I collagen, the main constituent of tendons. By then attaching each fibrous tissue to the artificial tendon tissue, it has become possible to stably create the fibrous tissues for production.”
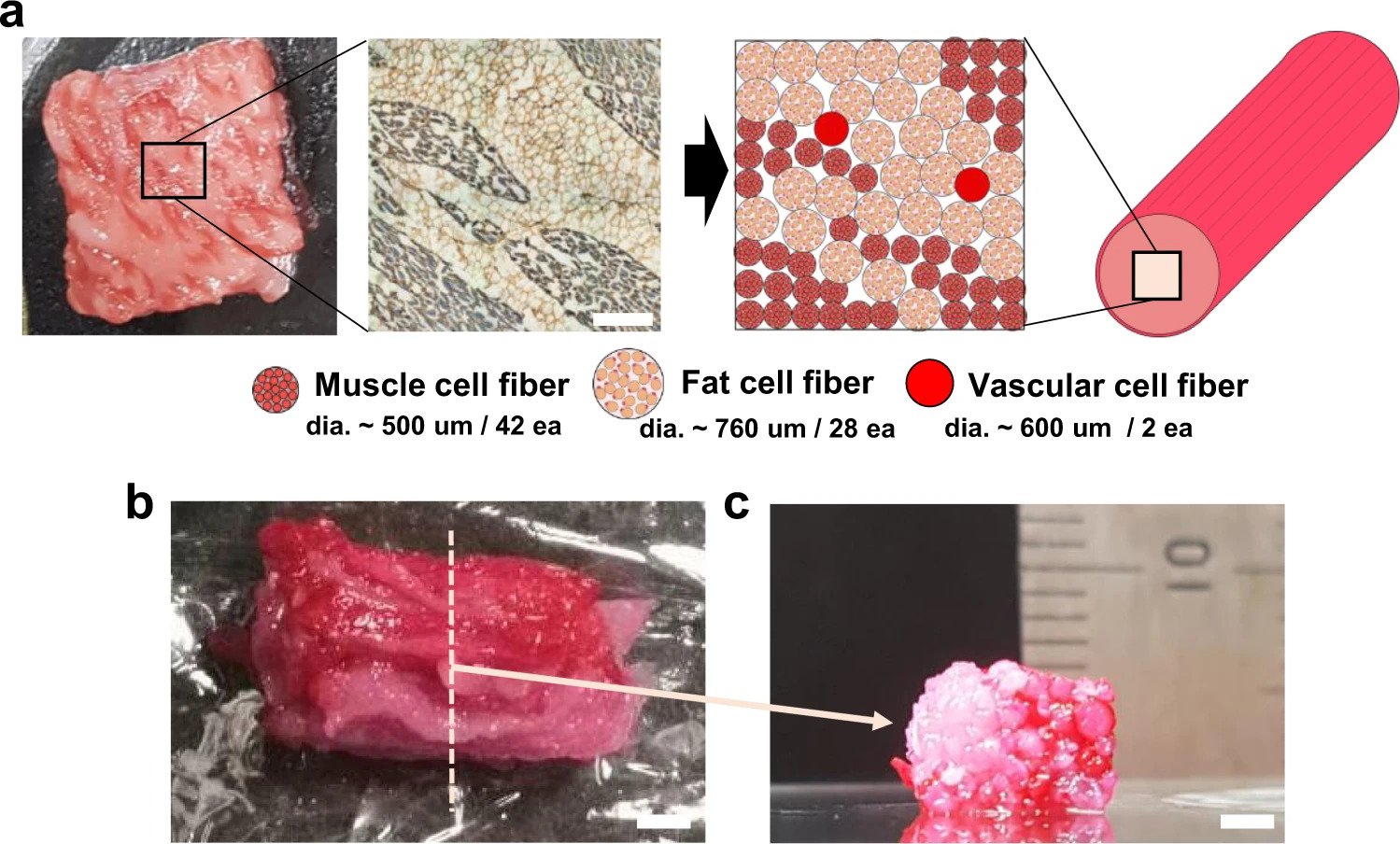
To accurately reproduce commercial Wagyu beef, the researchers took a cross-sectional image of a Wagyu cut to produce a model pattern that showed the required number of muscle, fat, and blood capillary cell fibers needed, as well as their arrangement. The cell fibers were obtained via the TIP process and were then stacked in line with the model image, before being treated with transglutaminase, a common food cross-linking enzyme, to accelerate the assembly process.
The Wagyu beef structure was constructed from a total of 72 3D printed bovine cell fibers, including 42 muscle fibers, 28 adipose tissues, and two blood capillaries.
随着肌肉,脂肪组织和血液毛细血管的比率在不同类型之间有所不同,研究人员的技术可以相应地打印不同类型的纤维,以准确复制其单个结构。例如,wagyu臀部由10.7%的脂肪组织组成,而wagyu sirloin占47.5%的脂肪组织,这将对这两种切割的质地和结构产生重大影响。
改善培养的肉类生产
According to the researchers, further improvement of their technology will not only make it possible to create complex meat structures that replicate the individual characteristics of different meat types and cuts, but also to control the fat and muscle content of cultured meat. Automated equipment for elements of the process other than 3D printing, such as cultivation, could also make it possible to produce cultured meat in any location.
因此,研究人员认为他们的技术可以帮助解决联合国(联合国)Sustainable Development Goals(SDGs) concerning environment preservations and resolving food crises. The research could also potentially help to negate the environmental destruction resulting from deforestation for the production of cereal grains needed for livestock farming, as well as ozone depletion caused by the CO2 emanating from livestock.
Additionally, producing cultured meat on-demand and in any location could have an energy-saving effect, as it can be created far quicker than the time it takes to grow cattle for slaughter.
Further information on the study can be found in the paper titled:“使用肌腱凝胶整合生物打印构成细胞纤维的整个切割肉样组织,”发表在《自然传播杂志》上。该研究由D. Kang,F。Louis,H。Liu,H。Shimoda,Y。Nishiyama,H。Nozawa,M。Kakitani,D。Takagi,D。Kasa,E。Nagamori,S。Irie撰写。,S。Kitano和M. Matsaki。
Subscribe to the3D打印行业通讯for the latest news in additive manufacturing. You can also stay connected by following us onTwitter并喜欢我们Facebook。
Looking for a career in additive manufacturing? Visit3D打印作业在行业中选择一系列角色。
订阅我们YouTube channelfor the latest 3D printing video shorts, reviews and webinar replays.
Featured image shows使用基于3D打印的原始组织建模技术生产的培养的和牛牛肉的制造过程和样品。图片通过Toppan。



