这2021 3D Printing Industry Awardsshortlists are open for voting, have your say now.
Welsh biotech firmsJellagenandCopner Biotechhave joined forces in what the companies are claiming is a “world-first” partnership to combine new bioinks derived from jellyfish collagen with advanced precision software.
Having secured funding of £123,724 from Wales’ business R&D investor scheme,聪明的cymru,合作伙伴正在寻求使用Jellagen的专有胶原蛋白0 Bioink和Copner Biotech的Advanced Advanced算法软件来提高3D生物打印的兼容性,可重复性和精度。
“We are absolutely delighted to partner with Jordan Copner and his team at Copner Biotech,” said Professor Andrew Mearns Spragg, Founder and Chief Scientific Officer at Jellagen. “SMART Cymru has enabled the creation of an exciting collaboration between two high-growth Welsh businesses at the forefront of exciting technological innovation in 3D software design capability and medical tissue engineering.”

Jellyfish collagen bioinks
Jellagen成立于2015年,目的是开发和商业化海洋生产的胶原蛋白,用于医学和科学研究领域的3D生物打印应用。该公司正在寻求为关键的生物材料建立可持续资源,这些生物材料不具有传统胶原蛋白来源的环境和人类健康风险。
这firm has been working on the development of its next-generation Collagen Type 0 bioink, derived from jellyfish collagen, and is looking to establish partnerships with medical institutions to investigate the material’s use as a treatment for skin diseases and tissue reconstruction.
这collagen in Jellagen’s biomaterial is extracted from Rhizostoma Pulmo, an ancient species of large jellyfish common to the Irish Sea. According to the firm, Collagen Type 0 has proven to promote anti-inflammatory tissue response that produces fewer side effects than traditional collagens derived from mammals, and demonstrates good compatibility and reproducibility for bioprinting applications.
Jellagen is currently marketing a range of Collagen Type 0 products for research use, and is also developing clinical-grade formulations for therapeutic and medical device applications. The firm’s current products include collagen-based gels, scaffolds, and collagen-coated cultureware plates.

Creating a “paradigm shift” in bioprinting
According to Jellagen and Copner Biotech, their new partnership has “the potential to transform the 3D bioprinting market”, which Verified Market Research’sGlobal 3D Bioprinting Market Reportpredicts will be worth £1.4 billion by 2028.
这partnership will see Jellagen’s Collagen Type 0 bioink combined with Copner Biotech’s advanced algorithm software to improve the precision of the 3D bioprinting process.
Copner Biotech于去年成立,目的是为3D细胞培养市场(例如癌症研究和组织工程)中的应用制造新的软件平台。此后,该公司开发了一个新颖的软件操作平台,用于设计促进氧气和营养梯度的细胞培养脚手架,并于今年早些时候颁发了GHP国际生命科学奖。
10月1日,Copner Biotech向英国知识产权办公室提出了一项申请,以专利设计和制造工作流,用于生产3D Bio脚手架,其细胞粘附对脚手架技术。展望未来,作为与Jellagen的新合作伙伴关系的一部分,Copner Biotech将寻求通过大众生产聚合物细胞支架和其他生物打印产品进一步开发和商业化其软件。
“This is a enormously exciting scientific collaboration between Copner Biotech and Jellagen, and a reflection of the increasing significance of 3D bioprinting in the global medical research landscape,” said Jordan Copner, Founder and CEO of Copner Biotech. “Our partnership aims to push the boundaries to advance innovation in biomedical engineering.”
Marine-inspired bioprinting
随着3D生物打印继续接收不断增长的兴趣和发展,科学家们越来越希望复制自然界中发现的材料和过程,这些材料和过程表现出了人造手段无法实现的理想特性。尤其是从海洋来源衍生的生物学和生物打印应用的发展引起了人们的极大兴趣,最近发生了一些研究突破。
例如,研究人员在Rutgers Universityhave3D打印的伪装准备软机器人inspired by the adaptable cells found in squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, whileYamagata Unviersityscientists have developed a 3D printed actuator that could form the basis of ajellyfish-like soft robot。
In June, scientists fromNorthwestern Universitydiscovered a rare type of iron mineral in the“流浪肉饼”软体动物的牙齿,并着手利用该发现来开发适合3D打印的生物学,以模仿软体动物手写笔的强度,刚度和结缔组织。最近,来自Pacific Northwest National Laboratory开发new seaweed-based bioinkthat can be integrated with fine mico pigment powders to produce vibrant colors well-suited to artistic applications.
摆脱生物学发展,hierarchical structure of limpetshas been harnessed for the design of 3D printed microneedle patches, and仿生细胞状结构具有独特的能量吸收能力已根据墨鱼的骨骼打印了3D。别处,龙虾壳图案have even formed the basis of designs for 3D printed concrete structures.

Subscribe to the3D打印行业通讯for the latest news in additive manufacturing. You can also stay connected by following us onTwitter并喜欢我们Facebook。
寻找一个职业在加法制造吗?6sit3D打印作业在行业中选择一系列角色。
订阅我们YouTube channelfor the latest 3D printing video shorts, reviews and webinar replays.
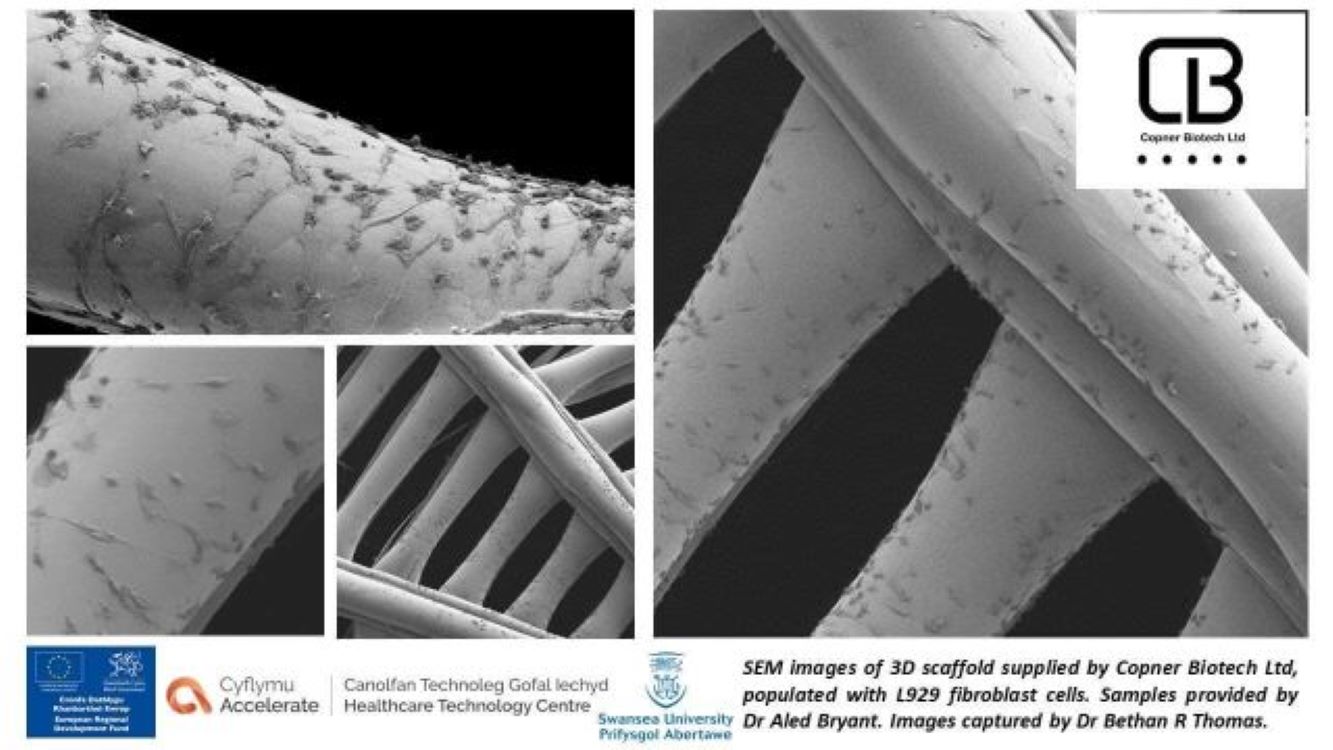
Featured image showsJellagen 3D支架创建了一个3D细胞培养环境,使细胞能够在体外模型系统中保持其体内形态,行为和反应能力。通过Jellagen的照片。



